“`html
Understanding Fan Airflow: Intake vs Exhaust
In the world of PC building and maintenance, managing airflow is critical to ensure optimal cooling and performance. One of the nuanced aspects of achieving efficient cooling lies in understanding fan dynamics – specifically, the difference between intake and exhaust fans. This blog post delves into the mechanics of airflow direction, positive vs. negative air pressure, and the roles of intake and exhaust fans. We will also explore how these factors interact with components like CPUs, GPUs, and liquid coolers. Additionally, we will provide insights into fan curves and the impact of case choices on airflow efficiency. Whether you are troubleshooting heating issues or optimizing a brand-new build, this guide offers a comprehensive look at maximizing your PC’s performance through strategic airflow management.
Airflow direction
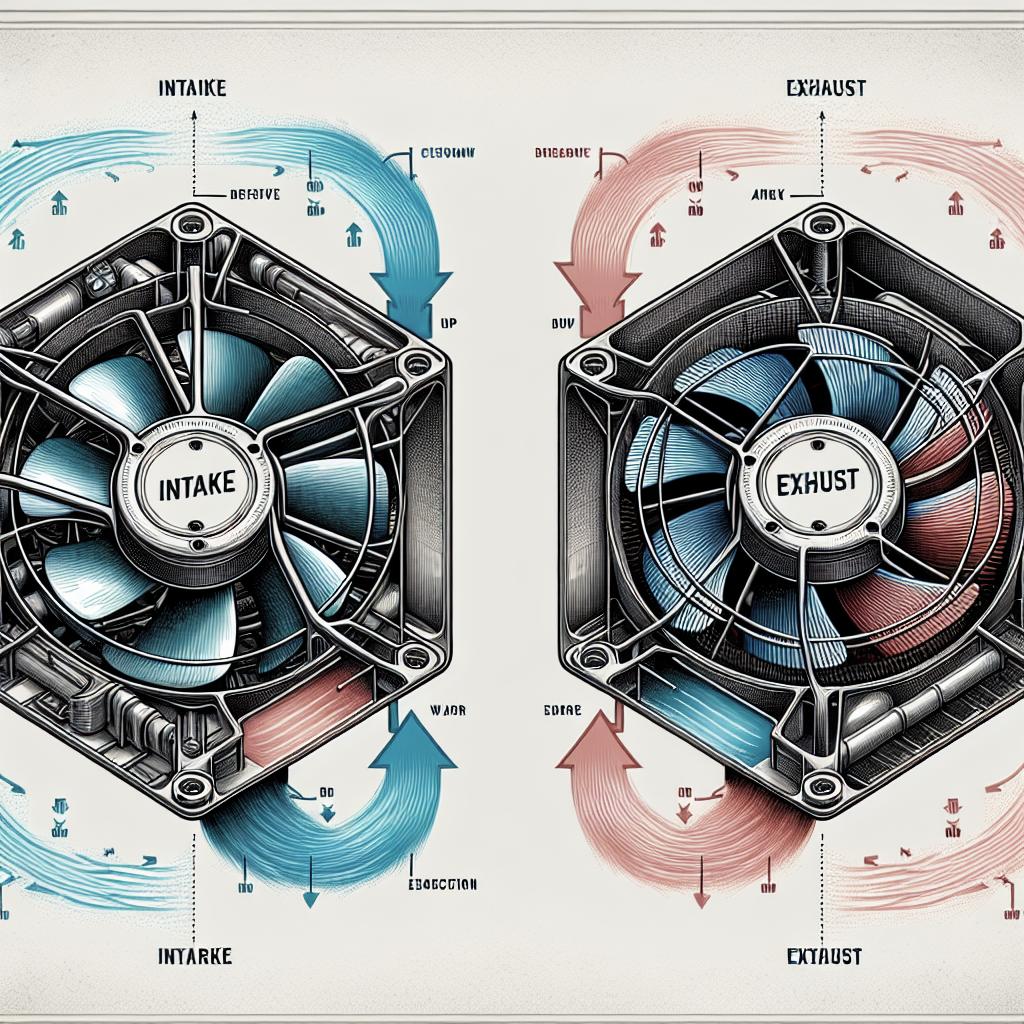
Understanding airflow direction is crucial for creating an effective cooling strategy in your computer system. Fans are designed to move air in a specific direction, generally marked on the fan itself with arrows indicating the airflow path. The direction of airflow affects how heat is dissipated; hence, it is important to orient fans correctly depending on whether they should be creating an intake or exhaust effect.
Typically, fan airflow is from the side with the protective grille or frame towards the label side. This rule of thumb helps in physically determining the airflow direction if the markings aren’t clear or present. Correctly placing fans to align with these airflow directions ensures consistent hot air expulsion and cooler air intake, thereby maintaining component efficiency.
Positive vs negative airflow
Positive airflow occurs when there are more intake fans than exhaust fans, which can help in reducing dust buildup inside the case by creating a slight pressure difference that expels contaminants. This pressure can leave dust settling mostly on intake filters instead of interior parts.
Conversely, negative airflow happens when the case has more exhaust fans. While potentially improving airflow efficiency by pulling more air through the case, it can increase dust accumulation inside. In general, achieving a balance—or slightly positive pressure—is ideal for most setups because it combines effective cooling with minimal dust entry.
Intake vs exhaust
Intake fans are responsible for pulling cool air into the case to prevent components from overheating, focusing on cooling critical components like the CPU and GPU. Ideally, they should be placed at the front or bottom of the case where they can draw in cooler ambient air.
Exhaust fans, on the other hand, push hot air out of the case, facilitating thermal regulation by removing heated air. The typical placement for exhaust fans is at the back or top of the case since hot air tends to rise, naturally aiding its expulsion.
be quiet! Pure Wings 2 120mm PWM (BL039) Cooling Fan
The be quiet! Pure Wings 2 120mm PWM fan exemplifies a versatile option for either intake or exhaust setups. Its robust design minimizes noise while offering high airflow capability, suitable for maintaining positive or negative pressure based on your configuration preference.
Particularly beneficial in quiet builds, it balances performance and acoustics efficiently. Users appreciate its high static pressure, ideal for overcoming airflow restrictions introduced by densely packed components or filters typically seen in more advanced or custom cases.
Push vs. pull for liquid coolers
In liquid cooling systems, the push vs. pull configuration affects thermal management significantly. A ‘push’ configuration means fans are placed to push air through the radiator towards the outside of the case, efficiently expelling warm air generated by the cooler.
Conversely, a ‘pull’ configuration has the fans drawing air through the radiator, which may offer quieter operation since fans won’t work against air pressure. Many liquid-cooling enthusiasts prefer a combined push-pull setup for maximum efficiency and performance, though this requires additional fans and can take up more space.
Case airflow and your CPU
The CPU is the heart of any computer system, and managing its temperature is vital for maintaining performance and longevity. Correctly configured case airflow directly impacts CPU temperature. Intake fans should direct cool air towards the CPU cooler, enhancing its ability to dissipate heat effectively.
Additionally, strategic placement of exhaust fans ensures that heat generated by the CPU doesn’t linger within the case, preventing temperature build-up. Case designs with unobstructed airflow paths greatly assist this, making certain that cooling isn’t hindered by other internal components.
How about your GPU?
The GPU, often running alongside the CPU as another heat source, requires similar attention to airflow to maintain optimal operation. Intake fans should align to provide a flow of fresh air directly to the GPU’s location within the case.
Depending on the type of GPU cooler (blower style vs. open-air), the number and placement of exhaust fans may need adjustment. Open-air cooled GPUs, for instance, benefit from numerous exhaust options that swiftly remove the hot air pushed into the case by the card’s fans.
Fan curves and case choice
Utilizing fan curves to adjust fan speeds dynamically based on temperature allows for an optimal balance between noise output and cooling efficiency. Fan control software can adjust RPMs to ramp up cooling under load without being overly loud during lighter use.
Furthermore, your choice of computer case can drastically influence airflow effectiveness. High airflow cases with mesh fronts can deliver superior cooling opportunities compared to cases focused on aesthetics or soundproofing, making the latter less effective without careful management of fan speeds and placement.
Corsair iCUE Commander PRO Smart RGB Lighting and Fan Speed Controller
The Corsair iCUE Commander PRO is a game-changer in terms of fan speed management, offering fine control over individual fan operations and reducing noise without sacrificing performance. Seamless integration with RGB lighting can enhance not only thermal control but also aesthetic appeal.
It allows complex setups with precise control over multiple fan and RGB channels, suiting users who desire a cohesive, customized cooling environment tailored to specific requirements and conditions, all accessible through the intuitive iCUE software.
Recent stories by Thiago Trevisan:
Thiago Trevisan’s recent articles provide deep insights into PC building and maintenance. Exploring the latest in thermal management solutions, Trevisan’s stories are packed with tips on optimizing computers for both performance enthusiasts and everyday users alike.
Covering topics like advanced cooling solutions and tech innovations, these stories offer valuable guidance for both seasoned builders and novices, helping them navigate the ever-evolving landscape of computer hardware with confidence.
| Key Concept | Details |
|---|---|
| Airflow Direction | Understanding fan orientation for effective thermal management. |
| Positive vs. Negative Airflow | Balancing intake and exhaust fans to manage internal pressure and dust. |
| Intake vs. Exhaust | Functional placement of fans to optimize cooling efficiency. |
| Push vs. Pull for Liquid Coolers | Configurations that impact cooling effectiveness for liquid systems. |
| CPU Cooling | Importance of directed airflow for CPU temperature control. |
| GPU Cooling | Strategic placement of fans around the GPU for optimal thermal management. |
| Fan Curves & Case Choice | Dynamic fan control and case selection for efficient airflow. |
“`